Kenya has unveiled its Digital Economy Blueprint anchored on five pillars as a guiding tool for the adoption of digital technologies for Africa’s transformation.
President Uhuru Kenyatta launched the blueprint-themed “powering Kenya’s transformation” at the Transform Africa Summit in Kigali, Rwanda.
He said “It is intended as a framework to guide us as we accelerate the adoption of digital technologies. I hope all countries will find value in contextualizing this framework to their specific ecosystems so as to realize the full potential of our digital transformation,” the President noted as he launched the blueprint at the Transform Africa Summit in Kigali.
Kenyatta said Kenya’s proactive digital economy strategy gives prominence to five pillars among them an infrastructure that is available affordable, resilient and reliable.
“Achieving ubiquitous, fast, and inexpensive internet connectivity for African businesses and households is critical to unlocking the potential of the digital economy. Connectivity needs to reach a certain threshold in order for users to access digital service,” said President Kenyatta.
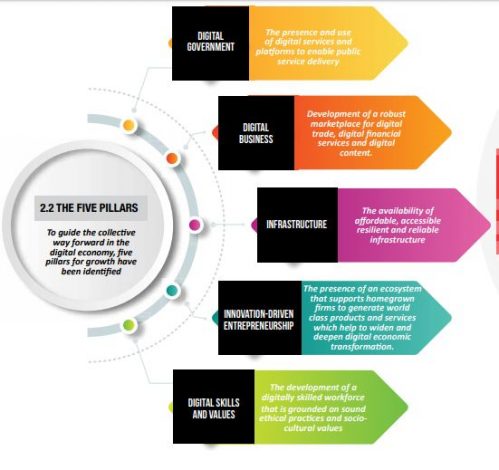 The Blueprint identifies the five pillars of the digital economy, which are described under the headings, Digital Government, Digital Business, Infrastructure, Innovation-Driven Entrepreneurship and Digital Skills and Values.
The Blueprint identifies the five pillars of the digital economy, which are described under the headings, Digital Government, Digital Business, Infrastructure, Innovation-Driven Entrepreneurship and Digital Skills and Values.
“There are four cross-cutting themes that are resident in every pillar, namely legal and policy frameworks, emerging technologies, interoperability and data,” reads part of the Blueprint.
The first pillar is the digital infrastructure, and the availability of affordable, accessible, resilient and reliable internet.
It gives focus on the development of a robust digital market characterised by the increased quality of financial inclusion, fair competition, resilient data infrastructure, advanced consumer protection, and greater regional integration. This pillar has three main focus areas namely: digital trade, digital financial services, and digital content.
The second pillar is the digital government, which describes the need for the presence and use of digital services and platforms to enable public service delivery.
Here, the government envisions adopting and implementing it to generate more revenue; reduce waste; improve Government services and efficiency; increase citizen participation in a transparent and trusted environment.
The third pillar is a digital business, which highlights the role of creating an enabling environment for developers and entrepreneurs to operate on e-platforms.
In this case, Digital skills will enable every Kenyan to have access to digital technology, have the literacy and know-how to use this technology, and be able to participate in and create with this technology.
The fourth pillar is innovation-driven entrepreneurship – the presence of the ecosystem that supports home-grown firms to generate world-class products and services.
The fifth pillar focuses on digital skills and values – critical to digital entrepreneurship, digital adoption and transformation, and the development of a digitally skilled workforce that is grounded on sound ethical practices and sociocultural values.





1 Comment
Pingback: Digital Economy: Kenya's ICT Ministry Launches White Paper on Talent Cultivation